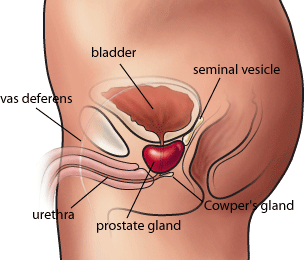
Prostate (from the Greek προστάτης - prostates, literally "one who stands before", "protector", "guardian" [1]) is a connection tubuloalveolar exocrine gland in the male reproductive system of mammals. Women do not have a prostate gland, although women are microscopic paraurethral Skene in the glands associated with the distal third of the urethra in prevaginal space, which are homologous to the prostate. The main function of the gland is to store and identify clear, slightly alkaline (pH 7.29) fluids, representing 10-30% of the volume of seminal fluid that, along with sperm, is a semen. The rest of the seminal fluid produced two fundamental bubbles. Alkalinity of seminal fluid helps neutralize the acidity vaginal tract, prolonging the service life of sperm. Prostate part of the urethra develops from the pelvis (center) of the urogenital sinus (endodermal origin). Endodermal outgrowths arise from prostate part of the urethra and grow in the surrounding mesenchyme. Glandular epithelium prostate different from those endodermal cells, as well as mesenchyme differentiates stroma in a dense and smooth muscle of the prostate. [2] prostate gland are modified wall proximal part of the male urethra and there is a 9 week embryonic life to the development of the reproductive system. Condensation mesenchyme, urethra and Wolffian channels leads to adult prostate gland, composite body composed of several glandular and not glandular components tightly fused in the overall capsule. In the prostate, the urethra from the bladder is called prostate urethra and merges with two ejaculatory ducts. (The male urethra has two functions: to urine from the bladder during urination and for the transport of semen during ejaculation.) Prostaty is sheathed in the pelvis floor muscles, which contract during ejaculatory process. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) occurs in older men, [6] prostate often extends to the point where it becomes quite difficult urination. Symptoms include not need to go to the toilet often (pollakisuria) or taking while to start (fluctuations). If the prostate grows too large it could restrict the urethra and impede the flow of urine, which makes urination difficult and painful and, in extreme cases absolutely impossible. BPH can be treated with medication, minimally invasive procedures or, in extreme cases, surgery that removing the prostate. Minimally invasive procedures include Transurethral needle ablation of the prostate (tuna) and Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT). These outpatient procedures could then include prostate temporary stent, in order to allow normal urination voluntarily, without worsening irritative symptoms [7]. Surgery most frequently used in such cases is called transurethral resection of the prostate (or TURP TUR). In TURP, the document is introduced through the urethra to remove prostate tissue that is pressing against the upper part of the urethra and restricting urine flow. Older men often have corpora amylacea [8] (amyloid), dense clusters of calcified proteinaceous material in the channels of their prostates. Corpora amylacea May impede lumens of prostate ducts, and may lie in some cases, BPH. Cancer of the prostate is one of the most common cancers affecting elderly people in developed countries and a substantial cause of death for older people (some specialists estimated at 3%). The regular rectal exams recommended for older men to detect prostate cancer early. In 1993, in the Journal of the American Medical Association have shown a link between vasectomy and an increased risk of prostate cancer. Reported studies on 48000 and 29000 men, who had vasectomies showed 66 per cent and 56 per cent higher than prostate cancer, respectively. The risk increases with age and number of years since the vasectomy was held. But in March the same year, the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development held a conference jointly to the National Cancer Institute and others to review available data and information on the relationship between prostate cancer and vasectomies. It was found that communication between the two was very weak, at best, even if with a vasectomy increased risk, the risk was relatively small. Recent scientific breakthroughs are now meant the use of prostate stent is a viable method prevents the spread of the prostate. The stent devices are inserted to expand his urethra and keep it open. The stent may be temporary or permanent, and this is mainly done on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia or spinal and usually takes about 30 minutes.
No comments:
Post a Comment